Product Description
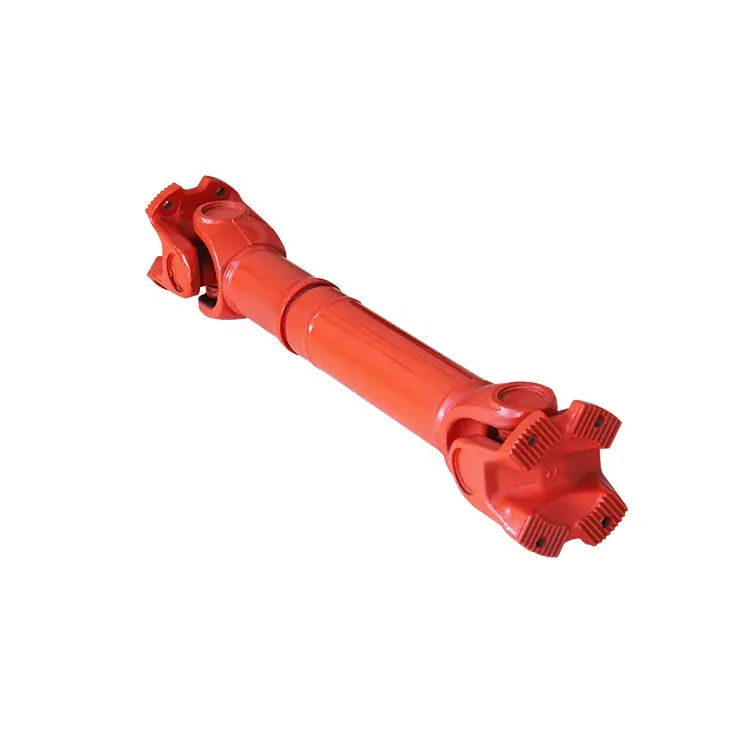
SWC Series-Medium-Duty Designs Cardan shaft
Designs
Data and Sizes of SWC Series Universal Joint Couplings
| Type | Design Data Item |
SWC160 | SWC180 | SWC200 | SWC225 | SWC250 | SWC265 | SWC285 | SWC315 | SWC350 | SWC390 | SWC440 | SWC490 | SWC550 | SWC620 |
| A | L | 740 | 800 | 900 | 1000 | 1060 | 1120 | 1270 | 1390 | 1520 | 1530 | 1690 | 1850 | 2060 | 2280 |
| LV | 100 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 140 | 140 | 140 | 140 | 150 | 170 | 190 | 190 | 240 | 250 | |
| M(kg) | 65 | 83 | 115 | 152 | 219 | 260 | 311 | 432 | 610 | 804 | 1122 | 1468 | 2154 | 2830 | |
| B | L | 480 | 530 | 590 | 640 | 730 | 790 | 840 | 930 | 100 | 1571 | 1130 | 1340 | 1400 | 1520 |
| M(kg) | 44 | 60 | 85 | 110 | 160 | 180 | 226 | 320 | 440 | 590 | 820 | 1090 | 1560 | 2100 | |
| C | L | 380 | 420 | 480 | 500 | 560 | 600 | 640 | 720 | 782 | 860 | 1040 | 1080 | 1220 | 1360 |
| M(kg) | 35 | 48 | 66 | 90 | 130 | 160 | 189 | 270 | 355 | 510 | 780 | 970 | 1330 | 1865 | |
| D | L | 520 | 580 | 620 | 690 | 760 | 810 | 860 | 970 | 1030 | 1120 | 1230 | 1360 | 1550 | 1720 |
| M(kg) | 48 | 65 | 90 | 120 | 173 | 220 | 250 | 355 | 485 | 665 | 920 | 1240 | 1765 | 2390 | |
| E | L | 800 | 850 | 940 | 1050 | 1120 | 1180 | 1320 | 1440 | 1550 | 1710 | 1880 | 2050 | 2310 | 2540 |
| LV | 100 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 140 | 140 | 140 | 140 | 150 | 170 | 190 | 190 | 240 | 250 | |
| M(kg) | 70 | 92 | 126 | 165 | 238 | 280 | 340 | 472 | 660 | 886 | 1230 | 1625 | 2368 | 3135 | |
| Tn(kN·m) | 16 | 22.4 | 31.5 | 40 | 63 | 80 | 90 | 125 | 180 | 250 | 355 | 500 | 710 | 1000 | |
| TF(kN·m) | 8 | 11.2 | 16 | 20 | 31.5 | 40 | 45 | 63 | 90 | 125 | 180 | 250 | 355 | 500 | |
| Β(°) | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| D | 160 | 180 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 265 | 285 | 315 | 350 | 390 | 440 | 490 | 550 | 620 | |
| Df | 160 | 180 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 265 | 285 | 315 | 350 | 3690 | 440 | 490 | 550 | 620 | |
| D1 | 137 | 155 | 170 | 196 | 218 | 233 | 245 | 280 | 310 | 345 | 390 | 435 | 492 | 555 | |
| D2(H9) | 100 | 105 | 120 | 135 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 185 | 210 | 235 | 255 | 275 | 320 | 380 | |
| D3 | 108 | 114 | 140 | 159 | 168 | 180 | 194 | 219 | 245 | 273 | 299 | 325 | 402 | 426 | |
| Lm | 95 | 105 | 110 | 125 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 180 | 195 | 215 | 260 | 270 | 305 | 340 | |
| K | 16 | 17 | 18 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 27 | 32 | 35 | 40 | 42 | 47 | 50 | 55 | |
| T | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 12 | 12 | |
| N | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | |
| D | 15 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 19 | 19 | 21 | 23 | 23 | 25 | 28 | 31 | 31 | 38 | |
| B | 20 | 24 | 32 | 32 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 50 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 100 | |
| G | 6.0 | 7.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 15.0 | 16.0 | 18.0 | 20.0 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 25 | |
| MI(Kg) | 2.57 | 3 | 3.85 | 3.85 | 5.17 | 6 | 6.75 | 8.25 | 10.6 | 13 | 18.50 | 23.75 | 29.12 | 38.08 | |
| Size | M14 | M16 | M16 | M16 | M18 | M18 | M20 | M22 | M22 | M24 | M27 | M30 | M30 | M36 | |
| Tightening torque(Nm) | 180 | 270 | 270 | 270 | 372 | 372 | 526 | 710 | 710 | 906 | 1340 | 1820 | 1820 | 3170 |
1. Notations:
L=Standard length, or compressed length for designs with length compensation;
LV=Length compensation;
M=Weight;
Tn=Nominal torque(Yield torque 50% over Tn);
TF=Fatigue torque, I. E. Permissible torque as determined according to the fatigue strength
Under reversing loads;
β=Maximum deflection angle;
MI=weight per 100mm tube
2. Millimeters are used as measurement units except where noted;
3. Please consult us for customizations regarding length, length compensation and
Flange connections.
(DIN or SAT etc. )
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Hollow Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What factors should be considered when selecting the right cardan shaft for an application?
When selecting a cardan shaft for a specific application, several crucial factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The following factors should be taken into account during the selection process:
1. Torque Requirements:
– One of the primary considerations is the torque requirements of the application. The cardan shaft should be capable of transmitting the required torque without exceeding its rated capacity. It is essential to determine the maximum torque that the shaft will experience during operation and select a cardan shaft that can handle that torque while providing an appropriate safety margin.
2. Speed and RPM:
– The rotational speed or RPM (revolutions per minute) of the application is another critical factor. Cardan shafts have specific rotational speed limits, and exceeding these limits can lead to premature wear, vibration, and failure. It is crucial to select a cardan shaft that is rated for the speed requirements of the application to ensure reliable and smooth operation.
3. Angle of Misalignment:
– The angle of misalignment between the driving and driven components should be considered. Cardan shafts can accommodate angular misalignment up to a certain degree, typically specified by the manufacturer. It is important to select a cardan shaft that can handle the anticipated misalignment angle to ensure proper power transmission and prevent excessive wear or binding.
4. Operating Conditions:
– The operating conditions of the application play a vital role in cardan shaft selection. Factors such as temperature, humidity, presence of corrosive agents, and exposure to vibration or shock need to be considered. It is crucial to select a cardan shaft that is designed to withstand the specific operating conditions to ensure durability and reliability.
5. Length and Size:
– The length and size of the cardan shaft should be chosen appropriately for the application. The length of the shaft affects its ability to absorb vibrations and accommodate misalignments. It is important to consider the available space and the required length to ensure proper fitment and functionality. Additionally, the size of the cardan shaft should be selected based on the load requirements and the available torque capacity.
6. Maintenance and Serviceability:
– Consideration should be given to the ease of maintenance and serviceability of the cardan shaft. Some applications may require regular inspection, lubrication, or replacement of certain components. It is beneficial to select a cardan shaft that allows convenient access for maintenance and incorporates features such as grease fittings or easily replaceable universal joints.
7. Cost and Budget:
– Finally, the cost and budget constraints should be taken into account. Different cardan shaft manufacturers and suppliers may offer varying prices for their products. It is important to balance the desired quality, performance, and durability of the cardan shaft with the available budget.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers and designers can select the right cardan shaft for the application, ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and reliability. Collaboration with cardan shaft manufacturers and suppliers can also provide valuable insights and assistance in making the appropriate selection based on the specific requirements of the application.
Are there any emerging trends in cardan shaft technology, such as lightweight materials?
Yes, there are several emerging trends in cardan shaft technology, including the use of lightweight materials and advancements in design and manufacturing techniques. These trends aim to improve the performance, efficiency, and durability of cardan shafts. Here are some of the notable developments:
1. Lightweight Materials:
– The automotive and manufacturing industries are increasingly exploring the use of lightweight materials in cardan shaft construction. Materials such as aluminum alloys and carbon fiber-reinforced composites offer significant weight reduction compared to traditional steel shafts. The use of lightweight materials helps reduce the overall weight of the vehicle or machinery, leading to improved fuel efficiency, increased payload capacity, and enhanced performance.
2. Advanced Composite Materials:
– Advanced composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass composites, are being utilized in cardan shafts to achieve a balance between strength, stiffness, and weight reduction. These materials offer high tensile strength, excellent fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance. By incorporating advanced composites, cardan shafts can achieve reduced weight while maintaining the necessary structural integrity and durability.
3. Enhanced Design and Optimization:
– Advanced computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation techniques are being employed to optimize the design of cardan shafts. Finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations allow for better understanding of the structural behavior, stress distribution, and performance characteristics of the shafts. This enables engineers to design more efficient and lightweight cardan shafts that meet specific performance requirements.
4. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing):
– Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is gaining traction in the production of cardan shafts. This technology allows for complex geometries and customized designs to be manufactured with reduced material waste. Additive manufacturing also enables the integration of lightweight lattice structures, which further enhances weight reduction without compromising strength. The flexibility of 3D printing enables the production of cardan shafts that are tailored to specific applications, optimizing performance and reducing costs.
5. Surface Coatings and Treatments:
– Surface coatings and treatments are being employed to improve the durability, corrosion resistance, and friction characteristics of cardan shafts. Advanced coatings such as ceramic coatings, diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings, and nanocomposite coatings enhance the surface hardness, reduce friction, and protect against wear and corrosion. These treatments extend the lifespan of cardan shafts and contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of the power transmission system.
6. Integrated Sensor Technology:
– The integration of sensor technology in cardan shafts is an emerging trend. Sensors can be embedded in the shafts to monitor parameters such as torque, vibration, and temperature. Real-time data from these sensors can be used for condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and performance optimization. Integrated sensor technology allows for proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving the overall operational efficiency of vehicles and machinery.
These emerging trends in cardan shaft technology, including the use of lightweight materials, advanced composites, enhanced design and optimization, additive manufacturing, surface coatings, and integrated sensor technology, are driving advancements in the performance, efficiency, and reliability of cardan shafts. These developments aim to meet the evolving demands of various industries and contribute to more sustainable and high-performing power transmission systems.
What is a cardan shaft and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A cardan shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or drive shaft, is a mechanical component used in vehicles and machinery to transmit torque and rotational power between two points that are not in line with each other. It consists of a tubular shaft with universal joints at each end, allowing for flexibility and accommodating misalignment between the driving and driven components. The cardan shaft plays a crucial role in transferring power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven machinery. Here’s how it functions in vehicles and machinery:
1. Torque Transmission:
– In vehicles, the cardan shaft connects the transmission or gearbox to the differential, which then distributes torque to the wheels. When the engine generates rotational power, it is transmitted through the transmission to the cardan shaft. The universal joints at each end of the shaft allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the suspension, axle movement, and road conditions. As the cardan shaft rotates, it transfers torque from the transmission to the differential, enabling power delivery to the wheels.
– In machinery, the cardan shaft serves a similar purpose of transmitting torque between the power source and driven components. For example, in agricultural equipment, the cardan shaft connects the tractor’s PTO (Power Take-Off) to various implements such as mowers, balers, or tillers. The rotational power from the tractor’s engine is transferred through the PTO driveline to the cardan shaft, which then transmits the torque to the driven machinery, enabling their operation.
2. Flexibility and Compensation:
– The cardan shaft’s design with universal joints provides flexibility and compensates for misalignment between the driving and driven components. The universal joints allow the shaft to bend and articulate while maintaining a continuous torque transmission. This flexibility is essential in vehicles and machinery where the driving and driven components may be at different angles or positions due to suspension movement, axle articulation, or uneven terrain. The cardan shaft absorbs these variations and ensures smooth power delivery without causing excessive stress or vibration.
3. Balancing and Vibration Control:
– Cardan shafts also contribute to balancing and vibration control in vehicles and machinery. The rotation of the shaft generates centrifugal forces, and any imbalance can result in vibration and reduced performance. To counterbalance this, cardan shafts are carefully designed and balanced to minimize vibration and provide smooth operation. Additionally, the universal joints help in absorbing minor vibrations and reducing their transmission to the vehicle or machinery.
4. Length Adjustment:
– Cardan shafts offer the advantage of adjustable length, allowing for variations in the distance between the driving and driven components. This adjustability is particularly useful in vehicles and machinery with adjustable wheelbases or variable attachment points. By adjusting the length of the cardan shaft, the driveline can be appropriately sized and positioned to accommodate different configurations, ensuring optimal power transmission efficiency.
5. Safety Features:
– Cardan shafts in vehicles and machinery often incorporate safety features to protect against mechanical failures. These may include shielding or guards to prevent contact with rotating components, such as the driveshaft or universal joints. In the event of a joint failure or excessive force, some cardan shafts may also incorporate shear pins or torque limiters to prevent damage to the driveline and protect other components from excessive loads.
In summary, a cardan shaft is a tubular component with universal joints at each end used to transmit torque and rotational power between non-aligned driving and driven components. It provides flexibility, compensates for misalignment, and enables torque transmission in vehicles and machinery. By efficiently transferring power, accommodating variations, and balancing vibrations, cardan shafts play a critical role in ensuring smooth and reliable operation in a wide range of applications.


editor by CX 2024-03-27