Product Description
Product Description
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | Parts | Auto Parts For Center Support Bearing | ||||||||
| Specification | Bearing ID 20-85mm | Trademark | YTK or Customized | |||||||
| Price | Negotiable | Transport Packing | Neutral Packing & Customized | |||||||
| Exportation | ZheJiang Port | Bearing Quality | ZV3 Level | |||||||
| Warranty | One Year or Above | Laser Mark | Available | |||||||
| Applicable Models | American Series | Production Capacity | 60, | Φ30 | CB | Φ35 Φ40 | 3535730 | Φ60 | ||
| Φ60 | Φ60 | 6 | Φ65 |
-FAQ:
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
Generally, we pack our goods in neutral boxes and brown cartons or as your demand.
If you have legally registered patent,we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of delivery?
EXW, FOB, CIF, CFR
Q3. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 10 to 30 days after receiving your advance payment.
The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Material: | Rubber |
| Transport Package: | as Your Demand |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
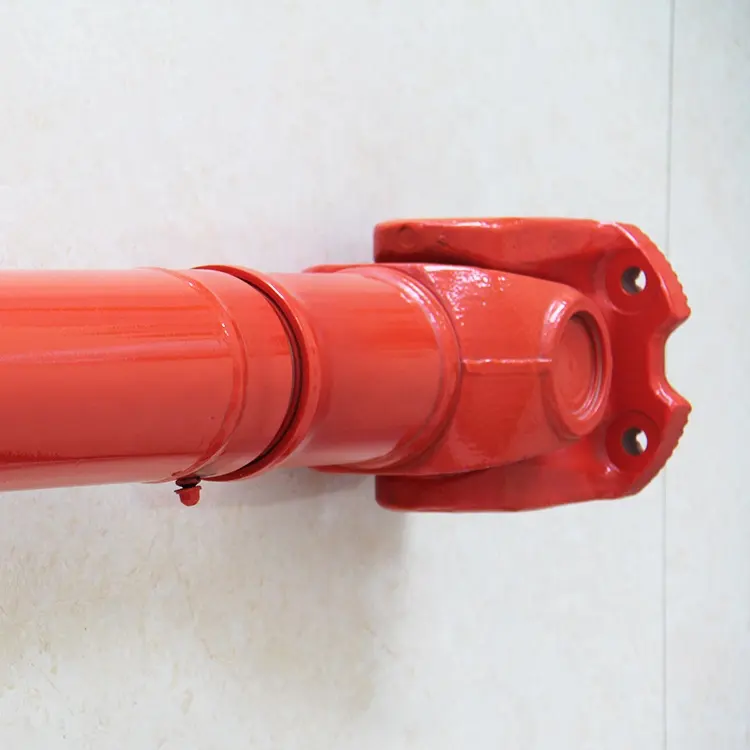

What maintenance practices are essential for prolonging the lifespan of cardan shafts?
Maintaining proper maintenance practices is crucial for prolonging the lifespan of cardan shafts and ensuring their optimal performance. Here are some essential maintenance practices to consider:
1. Regular Lubrication:
– Proper lubrication of the cardan shaft’s universal joints is vital for reducing friction, preventing wear, and ensuring smooth operation. Regularly lubricate the universal joints according to the manufacturer’s recommendations using the appropriate lubricant. This helps to minimize frictional losses, extend the life of the needle bearings, and maintain the efficiency of power transfer.
2. Inspection and Cleaning:
– Regular inspection and cleaning of the cardan shaft are essential for identifying any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the shaft for any cracks, corrosion, or excessive play in the universal joints. Clean the shaft periodically to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that could potentially cause damage or hinder proper operation.
3. Misalignment Adjustment:
– Check for any misalignment between the driving and driven components connected by the cardan shaft. If misalignment is detected, address it promptly by adjusting the alignment or replacing any worn or damaged components. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the shaft and its components, resulting in premature wear and reduced lifespan.
4. Balancing:
– Periodically check the balance of the cardan shaft to ensure smooth operation and minimize vibration. If any imbalance is detected, consult with a qualified technician to rebalance the shaft or replace any components that may be causing the imbalance. Balanced cardan shafts promote efficient power transfer and reduce stress on the drivetrain.
5. Torque and RPM Monitoring:
– Keep track of the torque and RPM (revolutions per minute) values during operation. Ensure that the cardan shaft is not subjected to torque levels exceeding its design capacity, as this can lead to premature failure. Similarly, avoid operating the shaft at speeds beyond its recommended RPM range. Monitoring torque and RPM helps prevent excessive stress and ensures the longevity of the shaft.
6. Periodic Replacement:
– Despite regular maintenance, cardan shafts may eventually reach the end of their service life due to normal wear and tear. Periodically assess the condition of the shaft and its components, considering factors such as mileage, operating conditions, and manufacturer recommendations. If significant wear or damage is observed, it may be necessary to replace the cardan shaft to maintain optimal performance and safety.
7. Manufacturer Guidelines:
– Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to your cardan shaft model. Manufacturers often provide detailed instructions regarding lubrication intervals, inspection procedures, and other maintenance requirements. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the maintenance practices align with the manufacturer’s specifications, promoting the longevity of the cardan shaft.
By following these essential maintenance practices, you can prolong the lifespan of cardan shafts, optimize their performance, and minimize the likelihood of unexpected failures. Regular maintenance not only extends the life of the cardan shaft but also contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the systems in which they are utilized.

How do cardan shafts handle variations in load, speed, and misalignment during operation?
Cardan shafts are designed to handle variations in load, speed, and misalignment during operation. They incorporate specific features and mechanisms to accommodate these factors and ensure efficient power transmission. Let’s explore how cardan shafts handle these variations:
1. Load Variation:
– Cardan shafts are designed to transmit torque and handle variations in load. The torque capacity of the shaft is determined based on the application’s requirements, and the shaft is manufactured using materials and dimensions that can withstand the specified loads. The design and construction of the shaft, including the selection of universal joints and slip yokes, are optimized to handle the anticipated loads. By choosing appropriate material strengths and dimensions, cardan shafts can effectively transmit varying loads without failure or excessive deflection.
2. Speed Variation:
– Cardan shafts can accommodate variations in rotational speed between the driving and driven components. The universal joints, which connect the shaft’s segments, allow for angular movement, thereby compensating for speed differences. The design of the universal joints and the use of needle bearings or roller bearings enable smooth rotation and efficient power transmission even at varying speeds. However, it’s important to note that excessively high speeds can introduce additional challenges such as increased vibration and wear, which may require additional measures such as balancing and lubrication.
3. Misalignment Compensation:
– Cardan shafts are specifically designed to handle misalignment between the driving and driven components. They can accommodate angular misalignment, parallel offset, and axial displacement to a certain extent. The universal joints in the shaft assembly allow for flexibility and articulation, enabling the shaft to transmit torque even when the components are not perfectly aligned. The design of the universal joints, along with their bearing arrangements and seals, allows for smooth rotation and compensation of misalignment. Manufacturers specify the maximum allowable misalignment angles and displacements for cardan shafts, and exceeding these limits can lead to increased wear, vibration, and reduced efficiency.
4. Telescopic Design:
– Cardan shafts often feature a telescopic design, which allows for axial movement and adjustment to accommodate variations in distance between the driving and driven components. This telescopic design enables the shaft to handle changes in length during operation, such as when the vehicle or equipment undergoes suspension movement or when the drivetrain components experience positional changes. The telescopic mechanism ensures that the shaft remains properly connected and engaged, maintaining power transmission efficiency even when there are fluctuations in distance or position.
5. Regular Maintenance:
– To ensure optimal performance and longevity, cardan shafts require regular maintenance. This includes inspections, lubrication of universal joints and slip yokes, and monitoring for wear or damage. Regular maintenance helps identify and address any issues related to load, speed, or misalignment variations, ensuring that the shaft continues to function effectively under changing operating conditions.
Overall, cardan shafts handle variations in load, speed, and misalignment through their design features such as universal joints, telescopic design, and flexibility. By incorporating these elements, along with proper material selection, lubrication, and maintenance practices, cardan shafts can reliably transmit torque and accommodate the changing operating conditions in vehicles and equipment.
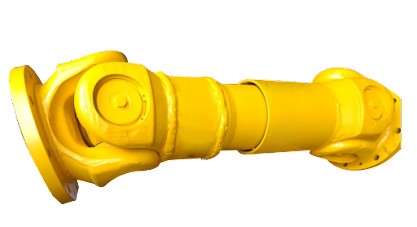
Can you explain the components and structure of a cardan shaft system?
A cardan shaft system, also known as a propeller shaft or drive shaft, consists of several components that work together to transmit torque and rotational power between non-aligned components. The structure of a cardan shaft system typically includes the following components:
1. Shaft Tubes:
– The shaft tubes are the main structural elements of a cardan shaft system. They are cylindrical tubes made of durable and high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum alloy. The shaft tubes provide the backbone of the system and are responsible for transmitting torque and rotational power. They are designed to withstand high loads and torsional forces without deformation or failure.
2. Universal Joints:
– Universal joints, also known as U-joints or Cardan joints, are crucial components of a cardan shaft system. They are used to connect and articulate the shaft tubes, allowing for angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. Universal joints consist of a cross-shaped yoke with needle bearings at each end. The yoke connects the shaft tubes, while the needle bearings enable the rotational motion and flexibility required for misalignment compensation. Universal joints allow the cardan shaft system to transmit torque even when the driving and driven components are not perfectly aligned.
3. Slip Yokes:
– Slip yokes are components used in cardan shaft systems that can accommodate axial misalignment. They are typically located at one or both ends of the shaft tubes and provide a sliding connection between the shaft and the driving or driven component. Slip yokes allow the shaft to adjust its length and compensate for changes in the distance between the components. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the distance between the driving and driven components can vary, such as vehicles with adjustable wheelbases or machinery with variable attachment points.
4. Flanges and Yokes:
– Flanges and yokes are used to connect the cardan shaft system to the driving and driven components. Flanges are typically bolted or welded to the ends of the shaft tubes and provide a secure connection point. They have a flange face with bolt holes that align with the corresponding flange on the driving or driven component. Yokes, on the other hand, are cross-shaped components that connect the universal joints to the flanges. They have holes or grooves that accommodate the needle bearings of the universal joints, allowing for rotational motion and torque transfer.
5. Balancing Weights:
– Balancing weights are used to balance the cardan shaft system and minimize vibrations. As the shaft rotates, imbalances in the mass distribution can lead to vibrations, noise, and reduced performance. Balancing weights are strategically placed along the shaft tubes to counterbalance these imbalances. They redistribute the mass, ensuring that the rotational components of the cardan shaft system are properly balanced. Proper balancing improves stability, reduces wear on bearings and other components, and enhances the overall performance and lifespan of the shaft system.
6. Safety Features:
– Some cardan shaft systems incorporate safety features to protect against mechanical failures. For example, protective guards or shielding may be installed to prevent contact with rotating components, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries. In applications where excessive forces or torques can occur, cardan shaft systems may include safety mechanisms such as shear pins or torque limiters. These features are designed to protect the shaft and other components from damage by shearing or disengaging in case of overload or excessive torque.
In summary, a cardan shaft system consists of shaft tubes, universal joints, slip yokes, flanges, and yokes, as well as balancing weights and safety features. These components work together to transmit torque and rotational power between non-aligned components, allowing for angular and axial misalignment compensation. The structure and components of a cardan shaft system are carefully designed to ensure efficient power transmission, flexibility, durability, and safety in various applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-07